Healthy Joint
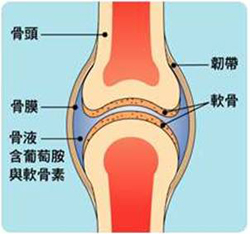
Joint is the connective tissue between two bones,
the major function of connective tissue is absorbing impact and lubricating.
Healthy cartilage
distribute on the interface of freely movable joints:
- Protect the bones and provide lubrication for them.
- Help joint move.
- Load body weight.
Components of cartilage:
- Water.
- Chondrocytes
- Extracellular matrix of chondrocytes
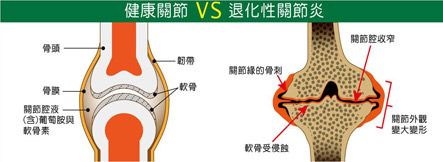
The degeneration of cartilage will lead to serious pain and damages due to the inflammation caused by reduction of lubrication between bones. This inflammation will become chronic and gradually worse. It is so called degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis (OA).
Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease in adults:
- There are 30% of 45~50 years old adults suffering from OA
- There are 50% of 50~65 years old adults suffering from OA.
- There are 80% of 65~75 years old adults suffering from OA.
The prevalence of OA at a younger age is increasing, especially in adults aged 35~45 years. OA is one of the major causes of disability.
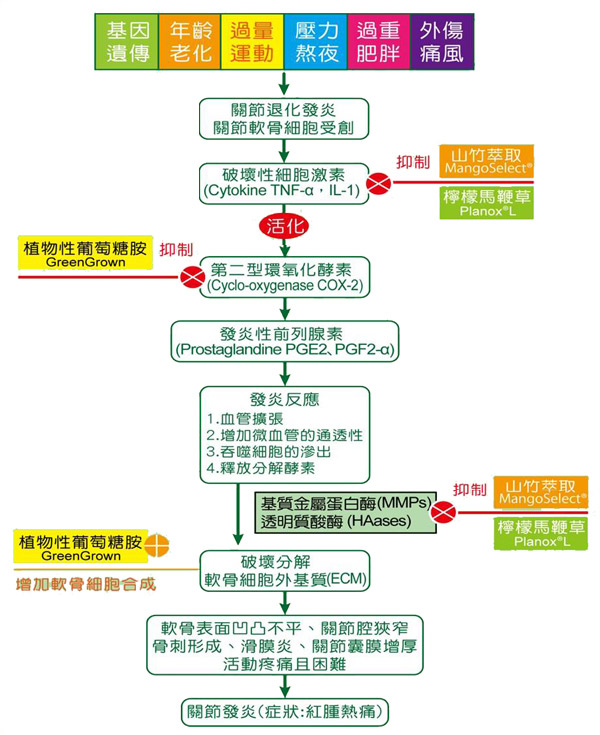
The cause of osteoarthritis
-
Primary osteoarthritis:
Above 50 years old
Genetics
Aging
Staying up and life pressures
Diabetes -
Secondary osteoarthritis:
Under 40 years old.
Injuries
Heavy, repeat mechanical stresses on joints
Gout
Avascular necrosis of the bone
Food habits
| Trigger finger | Osteoarthritis | Rheumatoid arthritis | Gout | |
| Causes | Damage of flexor tendon from repetitive, mechanical stress | Damage of cartilage from mechanical stress with insufficient self repair of joints leads to inflammation | Autoimmune | Poor uric acid metabolism |
| Susceptible individual | Above 45 years old | Elder women | Young women | Men |
| Lesions | The joint of fingers | The joints of knees, fingers, hip and spine. | The joints of knees, fingers, hip | Limbs and wrist joints |
| Symptoms | Straightening pain, stiffness. | Pain and stiffness exacerbate in cold days. | Pain and stiffness in the morning, systematic symptom. | Extreme pain on joints, burning sensations |
| Blood test | none | none | Rheumatoid factor,RF poistive | Blood uric acid >7 mg/ml |
| Sources: Kang-Hong Ming, director of family medicine clinic, hospital revitalization of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, MD, director Chen-Jian Cheng (United Daily News, Taiwan) | ||||
The pathological changes of osteoarthritis
The following pathological changes would happen when the cartilages degenerate.
- Uneven surfaces of cartilages
- Joint space narrowing
- Formation of bone spurs
- Synovitis
- Synovium of joints grow thicker.
- It’s hard to move joints because of pain.
Common lesions of Osteoarthritis:
The common lesions include the joints of hips, knees, back, fingers and neck.
Development of osteoarthritis
Symptoms of osteoarthritis:
- Inflammation: Redness, swelling, burning sensation, pain
- Tingling and numbness of joints.
- Loss of strength in joints.
- Crackling noise when joint moves.
- Joint swelling and deformation.
Treatments of osteoarthritis:
Medication:
NSAIDs(Side effects: Gastrointestinal discomfort, ulcers, bleeding, swelling hypertension, even kidney failure.)
COX-2 inhibiting drugs, DMOADs, Reconstitution of cartilages, Stem cells transplanting.
Non-medication:
Physical treatments, Rehabilitation, Appropriate exercise, Go on a diet, Acupuncture, Appropriate health supplements.
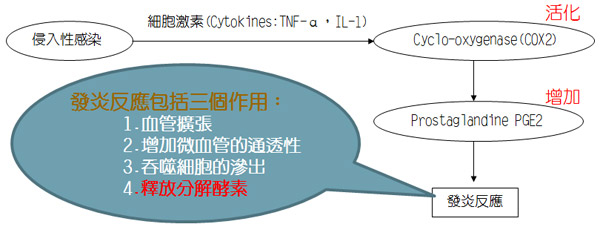
Pathogenesis of OA (i):
When cartilage was damaged, infected or stimulated; the destructive cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1) will activate the cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) which produces prostaglandine-2 (PGE-2) and prostaglandine-α (PGE-α) to promote inflammation.
Pathogenesis of OA (ii):
The inflammation of joint leads to the recruitment of macrophages to kill the invasive bacteria and to release degradative enzymes to degrade the extracellular matrix (ECM) of chondrocytes. These results in a vicious cycle of inflammation and end up with degenerative osteoarthritis.
Extracellular matrix, ECM, is degraded by degradative enzymes.
The catabolism and anabolism of extracellular matrix, ECM, are not balanced.
The degradative enzymes include:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs):
It can break down the collagens in ECM
-
Hyaluronidases (HAases):
It can break down the hyaluronic acids in the cartilage.