The physiology and infection of female urinary and genital tract
The physiology of urinary system:
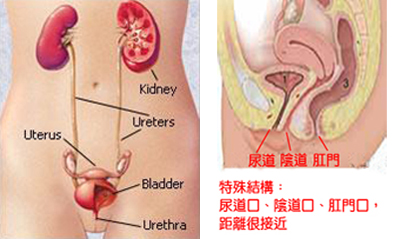
Kidney, ureter, bladder, and urethra.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI):
The inflammation of urinary system caused by bacterial infection.
UTI can be classified into:
Upper urinary tract infection: acute pyelonephritis.
Lower urinary tract infection: cystitis and urethritis.
The physiology of female genital tract:
Vagina, cervix, uterus.
Vaginal infection:
The imbalance in vaginal bacteria, changes in vaginal pH (normal pH range: 3.8-4.2), infection by bacteria, yeast or fungus.
Vaginal infection is the disruption of the healthy vaginal microbiota, common causes are:
- A: Microorganisms:
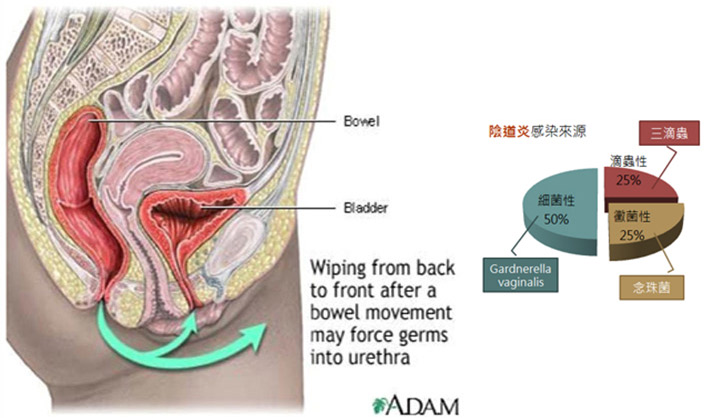
Candidiasis: vaginitis caused by proliferation of Candida albicans
Bacterial vaginosis: vaginitis caused by increased growth of Gardnerella vaginalis
Trichomoniasis: caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis - B: Changes in vaginal environment:
Disruption of the healthy vaginal microbiota: Inappropriate vaginal douching
Changes in vaginal pH: Sexual behavior, pregnancy or menopause. - C: Recurrent infection:
Cervicitis, erosion of cervix
cervical endometritis in aging women
Postoperation, catheter ablation or drug treatments.
Major causes of vaginal infection
Symptoms of vaginal infection
| Bacterial vaginitis | Candidiasis | Trichomoniasis | |
| Pathogens | Gardnerella vaginalis | C. albicans | Trichomonas |
| Color of vaginal discharge | Gray | White | Yellow, green, even dark red |
| Smell of discharge | Fishy smell | Not obvious | Foul-smelling |
| Appearance of discharge | Sticky | Cottage cheese-like | Foamy, with pus |
| Itchy | NO | YES | YES |
| Frequent urination, burning sensation | Mild | YES | YES |
| Redness, swelling, pain | Mild | YES | YES |
| Cervical bleeding | NO | NO | YES Yes, petechial hemorrhage (dot-like bleeding) |
Major causes of urinary tract infection:
- A. Physiological:
The close proximity of the urethral and vaginal openings and short urethra in females increase the risk of infection during sexual behaviors, pregnancy, and giving birth. - B. Urine contamination
- 1. Coughing or sneezing puts pressure on the bladder and cause urine leakage. If urine flow back up into bladder may cause infection.
- 2. Congenital anomalies in urinary tract, e.g. valvular stenosis.
- C. Hygiene habits:
Always wipe in the opposite direction of the urethra to decrease risk of infection. Wipe from the back to the front after using the bathroom increases the risk. - D. Invasive treatments:
For example, urinary catheter contamination. - E. Metabolic disorders:
For example: diabetes.
Major causative agent of urinary tract infection:
Approx. 90% cases of urinary tract infection were caused by E. coli.
- ◎Symptoms of infection:
- ◎Tingling, burning urination
- ◎Micturition (frequent urine), nocturnal enuresis
- ◎Cloudy urine
- ◎Bladder pain
- ◎Pain in lower back
- ◎Hematuria (urination with blood)
- ◎Difficult urinating
- ◎Smelly discharge
The common treatments for urogenital infection:
Antibiotics, oral.
Antibiotics, suppository.
Topical ointment.
The disadvantages of antibiotics:
- Antibiotic resistances
- Side effects
- Disrupt normal microbiota
★ The fundamental treatment for urogenital infection: ★
Establish of lactic acid bacteria in urethral and vaginal openings, restore normal microflora.
Why the urogenital infections in women are common in Taiwan?
First of all, because of the subtropical weathers, humidity and high-temperature lead to the growth of pathogens.
Second, eastern women feel embarrassed and are more conservative regarding urogenital problems. Refuse to see a doctor is common. Instead of seeking for medical treatments, inappropriate vaginal douching is common and may lead to exacerbation.
During pregnancy, the vaginal pH will change dramatically, which may lead to fungal infection.
Recurrences of urogenital infections are common.
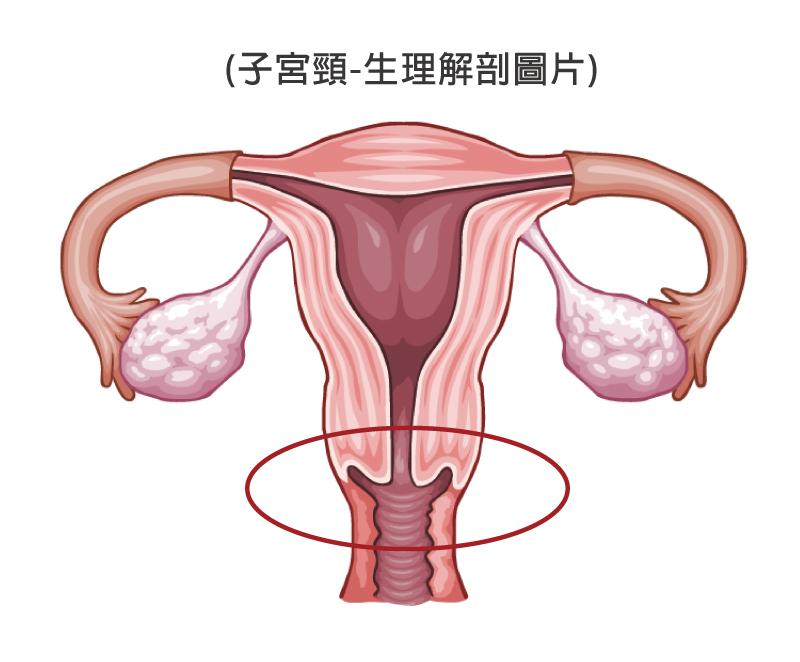
Understand cervix:
Length of normal cervix is about 3 cm. Cervix connects vagina with uterus.
It is the lower narrower part of the uterus. The lower end of the cervix bulges through the anterior wall of the vagina. The epithelial cells in cervix are susceptible to external stimulations which may lead to abnormal growth of cells, in other words, cervical cancer.
Common diseases of cervix
Cervicits:Most cervivits were caused by vaginitis. Vaginitis was caused by pathogens (e.g. C. albicans and HPV) which may further lead to carcinogenesis.
HPV infection::HPV is involved in the development of cervical cancer. Most cases of cervical cancer were caused by infections with HPV type 16, 18. The HPV types 45, 31, 33, 58, 52 are classified as high-risk types.
Onset stage of cervical cancer
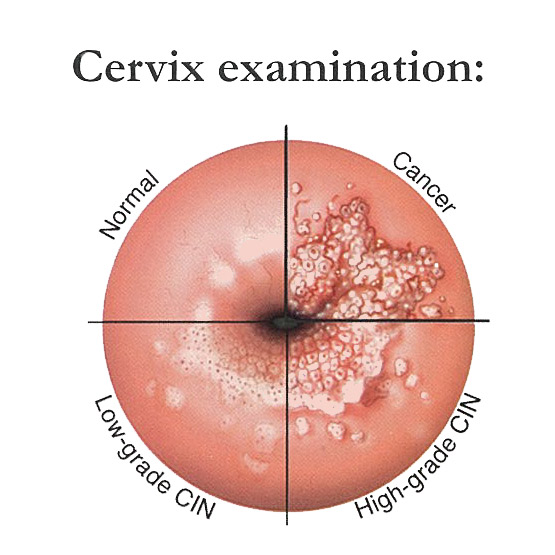
The carcinogenesis of cervical epithelial cells takes tens of years for developing carcinogenesis; this period is called “Onset stage”, also called “SIL (Squamous cell intraepithelial lesion)” or “CIN (Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia)”.
SIN and CIN are measurements for cervical cancer development stage.
SIN is for the cervical smear test
CIN is for pathological diagnoses.
If we can diagnose and treat before onset stage, we can prevent fatal cancer invasion.
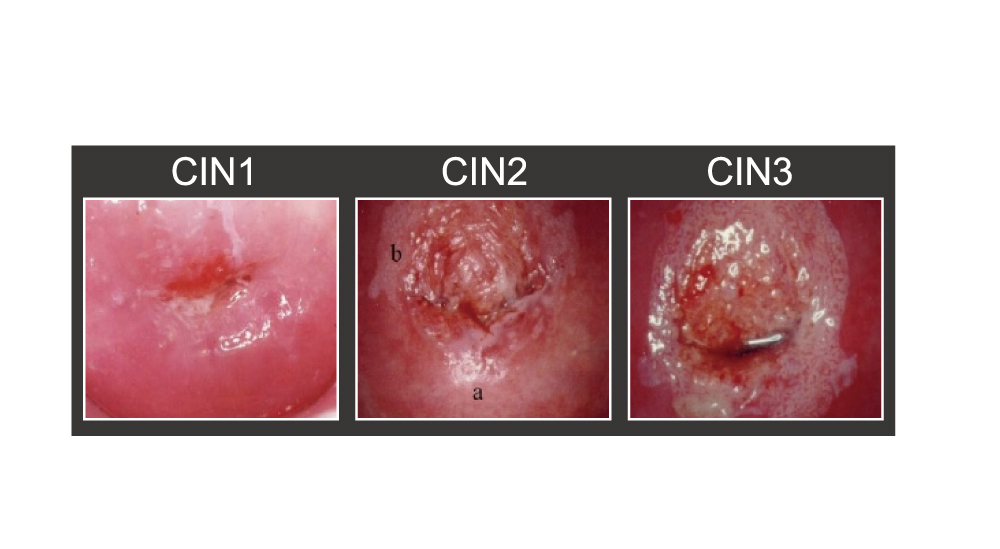
CIN 3 stage
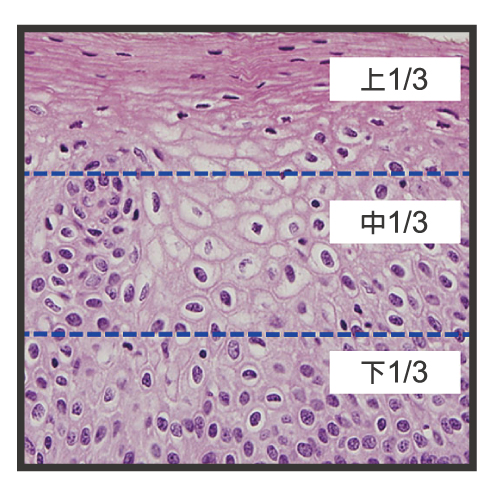
According to the morphology of cells:
-
CIN1:abnormal cells in one third of the thickness of the skin covering the cervix.
-
CIN2:abnormal cells in two third of the thickness of the skin covering the cervix.
-
CIN3:abnormal cells in full thickness of the skin covering the cervix.